Manufacturers of machinery used in various industries have been focusing their attention on the production of modular construction machines for many years. As a user, we get a machine in a basic configuration, and then, depending on our application and needs, we expand the purchased device with dedicated modules or tools specialized for a specific range of work.
For example, the selection of an appropriate tool used in a CNC machine allows for optimal use of its capabilities and adaptation to our application. The modular construction of the 3D printer is based on similar assumptions.
Modular solutions are increasingly used by machine manufacturers because they are much more practical and, what is more, they are in line with the idea of Industry 4.0. The user can have a machine that is flexible enough to adapt to changing expectations and different applications. The ability to upgrade the machine during its life cycle and the quick installation of other accessories such as specialized tools or modules is a great added value for any industrial class machine.
Manufacturing companies all over the world are increasingly equipping their machine parks with industrial 3D printers. For instance, 3D printing technology is being used to produce railway equipment, aircraft manufacturers replace metal components with materials like PEEK, ULTEM™, PC or PEKK-CF that are lighter yet resistant for various environmental factors. What’s more, the automotive industry makes numerous prototypes much faster and produces the jigs & fixtures using additive manufacturing.
The range of engineering and high-performance 3D printing materials available on the market is very wide and is still being developed. Work with filaments resistant to high temperatures and chemicals with extraordinary mechanical properties opens up opportunities for new applications in many industries. Engineers from various departments, including R&D, want to be able to work with the full range of available filaments using one 3D printer. Unfortunately, this is not always possible, because additive manufacturing machines have some limitations that reduce the scope of their work, for example, materials available for use.
Get the 3D printed parts you need just in time
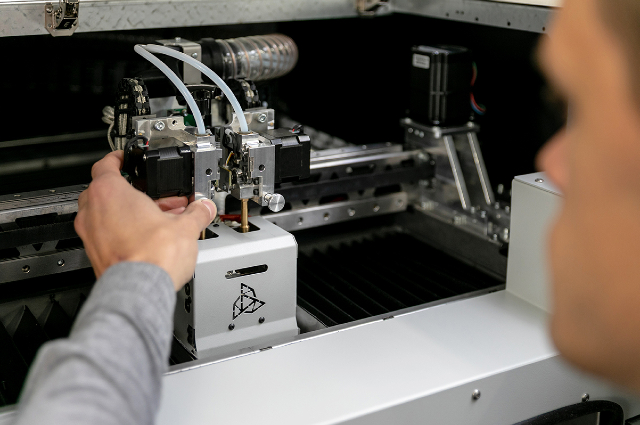


What are the must-have features for a 3D printer capable of producing parts from high-temperature materials such as PEEK, ULTEM™ , or PC to reinforced or flexible filaments? Find out more about why the industrial 3D printer should have a modular system.
There are many 3D printers on the market today, which work with a very narrow range of materials. It is associated with the need to have several different devices, each one for different applications. Such a situation results in increased purchase costs of a machine. Moreover, customer resources are used inefficiently. How does it look in practice?
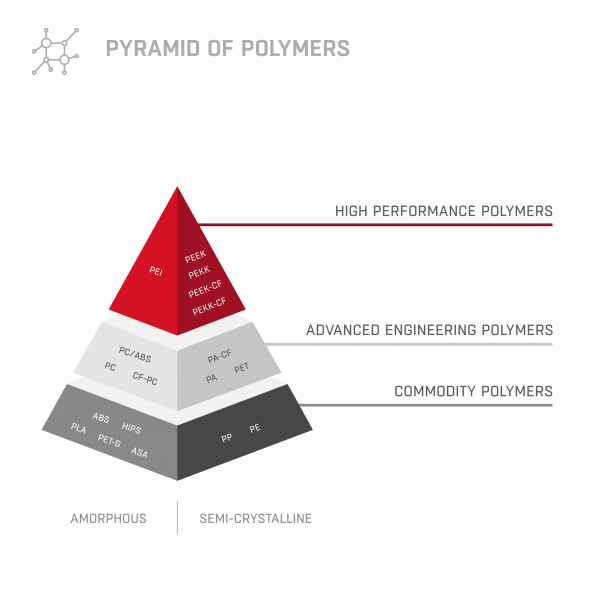
To 3D print a part with ABS, a low extrusion temperature material from a group of basic polymers used in 3D printing (the so-called Commodity), we need to use one 3D printer. When we want to produce parts with carbon fiber reinforced materials such as PA-CF or PC-CF, we need a second 3D printer, usually much more expensive. On the other hand, if we want to print models from a group of high-performance materials with high mechanical properties that will be resistant to high temperatures and chemicals, we have to equip our machinery park with another 3D printer. There are few devices on the market that work with such filaments as PEEK, PEKK, or ULTEM™. Printing with these materials requires specific temperatures and conditions e.g. actively heated chamber.
The 3D printing process must be adapted to the specific material, and one of the main parameters of this process is the extrusion temperature of the material, which is directly related to material thermal parameters like glass transition temperature or softening temperature. For example, PEEK requires the hotend to be heated between 360°C and 400°C to be extruded in the 3D printing process, while ABS needs only around 230°C to 260°C. Every standard 3D printer will have the problem to extrude so vastly different materials on one hotend.
The 3D printer’s modular construction allows you to purchase a single machine, which will allow you to print from multiple materials from different groups and receive models of very high quality.
Even when using the device most of the time to print basic materials such as ABS or PLA, you may need to 3D print parts from more durable materials such as PEEK or carbon/glass fiber reinforced materials. In case of a modular 3D printer, there is no need to purchase another device. Thanks to that solution you can upgrade your current machine and add other printing modules customized to a specific group of materials to optimize the printing process. The cost of purchasing the module is often many times lower than buying another 3D printer. Each module is customized to a specific group of materials in order to optimize the printing process.
Each change of extruded material to the other one with different properties may cause the clog of a printing nozzle. If we made a print using PEEK material and immediately afterward trying to print from PLA (the extrusion temperature of this material is much lower in comparison to PEEK), the remains of PEEK material would make printing with PLA impossible. On the other hand, trying to print material with low extrusion temperature at higher temperatures will lead to its degradation. As a result, the mechanical properties of the material and its resistance to external factors may be significantly reduced or lost. A great convenience for the user is the possibility to purchase a 3D printer equipped with a modular system that solves this problem.
The system of interchangeable printing modules allows the use of a wide range of materials on one machine. From commodity materials, which are widely used in the industry for rapid prototyping, to engineering and high-performance filaments for custom applications.
The construction of each module is dedicated to a specific group of materials and its characteristics to optimize the 3D printing process as much as possible. To obtain the best print quality and details it is necessary to adapt the printing process to the specific material. Each part should be printed from material with properties that are appropriate for its working environment (e. g. high chemical or mechanical resistance).

Fast module replacement depending on the required material you want to use
If you implement new materials from other groups into your production processes (see the polymer pyramid), you can upgrade your printer with other modules at any time.
To print from a wide range of materials you do not need to buy a new 3D printer, just replace the module. This is a much more practical and economically efficient solution
To maintain the highest efficiency of the printing process, use a module designed for a specific group of materials. This enables you to obtain repeatable and dimensionally compatible prints on each of the available modules.
No need to use any additional accessories, the swap can be done without any tools.
Get the 3D printed parts you need just in time
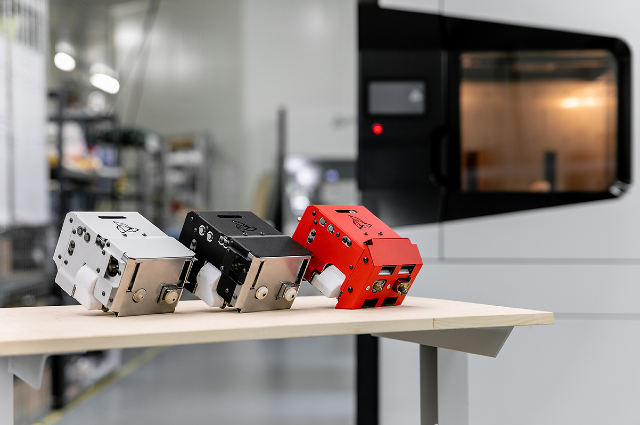

This feature makes it easier for users to work with the machine. Each module is equipped with an integrated tensometric system responsible for autocalibration measurements. Thanks to the automatic calibration system, even the slightest curvature or deflection of the heatbed from the level are continuously compensated by the 3D printer during the printing process. What’s more, each module is also equipped with EEPROM memory. The offset calibration values for this module are saved in the memory. Thanks to that these values do not have to be additionally measured and saved after module replacement, which allows for the quick start of work with the machine.
You can upgrade your 3D printer and add chosen modules designed for printing with other materials you need. The purchase of other modules may be postponed.
Each module is equipped with two hotends, which enables printing with model and support material (soluble or breakaway). The complete mechanism, thanks to its driving servomechanism, is able to automatically switch the printer between one of the two materials in less than 1 second.
The modules contain the active print cooling system, which is the basic method of preventing the warping phenomenon – the curling of the print corners up. In extreme cases, it may lead to major printing failure and always adversely affects the appearance, especially the bottom of the print surface.

Printing modules M280, M360, and M500 are interchangeable accessories of industrial 3D printers – 3DGence INDUSTRY F421. Each module is equipped with two printheads, which consist of a heating block and an exchangeable printing tip.
The numerical values in the module names define the maximum operating temperature of the module. Each of them is adapted to print from a different group of materials.
Up to 280°C
Up to 360°C
Up to 500°C
ABS, ASA, PLA, PA6
PC, ULTEM
PEEK, PEKK
Industrial 3D printer can be a complementary machine that will support traditional manufacturing processes. Choosing a proper machine that will suit your needs is not an easy task.
If you would like to know more what industrial 3D printer will be proper for your company, you can consult with 3D printing experts: [email protected]
